LoRA-Whisper: A Scalable and Efficient Solution for Multilingual ASR
1. Background & Motivation
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) has made significant strides in recent years, particularly with the rise of large-scale multilingual models like OpenAI’s Whisper, Google USM, and Meta’s MMS. These models unlock possibilities for building speech recognition systems that support dozens — or even hundreds — of languages.
However, building such multilingual ASR systems remains challenging due to:
- Language Interference: When multiple languages are trained in a shared model, performance may degrade due to data imbalance, dialectal accents, and language similarities.
- Catastrophic Forgetting: Fine-tuning a model on new languages often causes the model to forget previously learned languages, severely impacting recognition performance.
2. The Proposed Solution: LoRA-Whisper
To tackle these two key challenges, researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Tencent AI Lab introduce LoRA-Whisper, a parameter-efficient and extensible multilingual ASR framework based on the Whisper model and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA).
What is LoRA?
LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) is a lightweight fine-tuning technique that freezes the original model weights and injects small, trainable low-rank matrices into certain layers (e.g., attention and feed-forward layers). This allows models to be efficiently adapted to new tasks or domains with minimal parameter overhead.
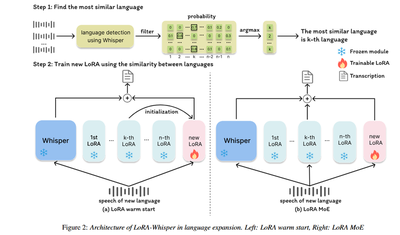
How LoRA-Whisper Works
- For each language, a language-specific LoRA module is attached to the Whisper model.
- The Whisper model remains frozen, serving as a shared backbone.
- When recognizing a language, only the corresponding LoRA module is activated during inference.
- This design prevents language interference and ensures knowledge preservation of all previously learned languages.
Adding New Languages (Language Expansion)
LoRA-Whisper offers two innovative methods for expanding the model with new languages without retraining the entire model:
- LoRA Warm Start: The LoRA module for a new language is initialized using the LoRA module of the most similar existing language (based on Whisper’s language ID probabilities).
- LoRA Mixture of Experts (MoE): The system dynamically selects and combines LoRA modules from multiple similar languages during training and inference to aid the new language’s learning.
3. Experimental Results
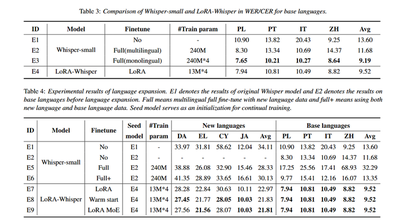
Experiments were conducted using MLS and FLEURS datasets across 8 languages. Highlights include:
- Multilingual ASR: LoRA-Whisper outperformed multilingual fine-tuning and came close to monolingual fine-tuning, using only ~5% of the trainable parameters.
- Language Expansion: Full fine-tuning with new languages caused up to 3× performance drop on existing languages. LoRA-Whisper maintained performance on existing languages while significantly improving WER (Word Error Rate) on new languages. LoRA warm start and LoRA MoE achieved 23% and 5% relative gains respectively over LoRA without similarity-based strategies.
Ablation Study: Does Language Similarity Help?
Yes. The authors demonstrated that initializing a new language’s LoRA from a similar language’s LoRA consistently led to better performance. In contrast, initializing from an unrelated language could hurt performance — even worse than training from scratch.
Limitations & Future Work
While LoRA-Whisper is scalable and efficient, one limitation is that model size increases linearly with the number of supported languages due to separate LoRA modules. Future directions include:
- Sharing LoRA modules among similar languages.
- Extending the approach to low-resource and code-switching scenarios.
- Integrating more advanced expert routing techniques.
4. Conclusion
LoRA-Whisper offers a compelling solution for building scalable, customizable, and language-resilient ASR systems. By combining Whisper’s robust multilingual backbone with the adaptability of LoRA, the paper demonstrates an effective way to expand and maintain large ASR systems without catastrophic forgetting or performance trade-offs. This work marks a step forward in enabling more inclusive, efficient, and modular speech recognition systems — critical for real-world multilingual applications.